
Top Effective Methods for Softening and Reducing Water Hardness
Water hardness is a significant factor affecting daily activities, industrial production, and equipment operation. Treating hard water not only helps protect equipment but also improves the quality of life. Below are the most effective methods for softening and reducing water hardness today.

1. Ion Exchange Method
1.1. Using Ion Exchange Resin
- How it works: Ion exchange resin (cation resin) replaces calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺) ions in water with sodium (Na⁺) ions.
- Advantages: High efficiency, suitable for various types of hard water. Easy-to-operate system, regenerable with salt (NaCl).
- Disadvantages: Requires periodic replenishment of regeneration salt.
1.2. Application in Large Systems
- Commonly used in industrial water treatment systems, boilers, and RO systems.
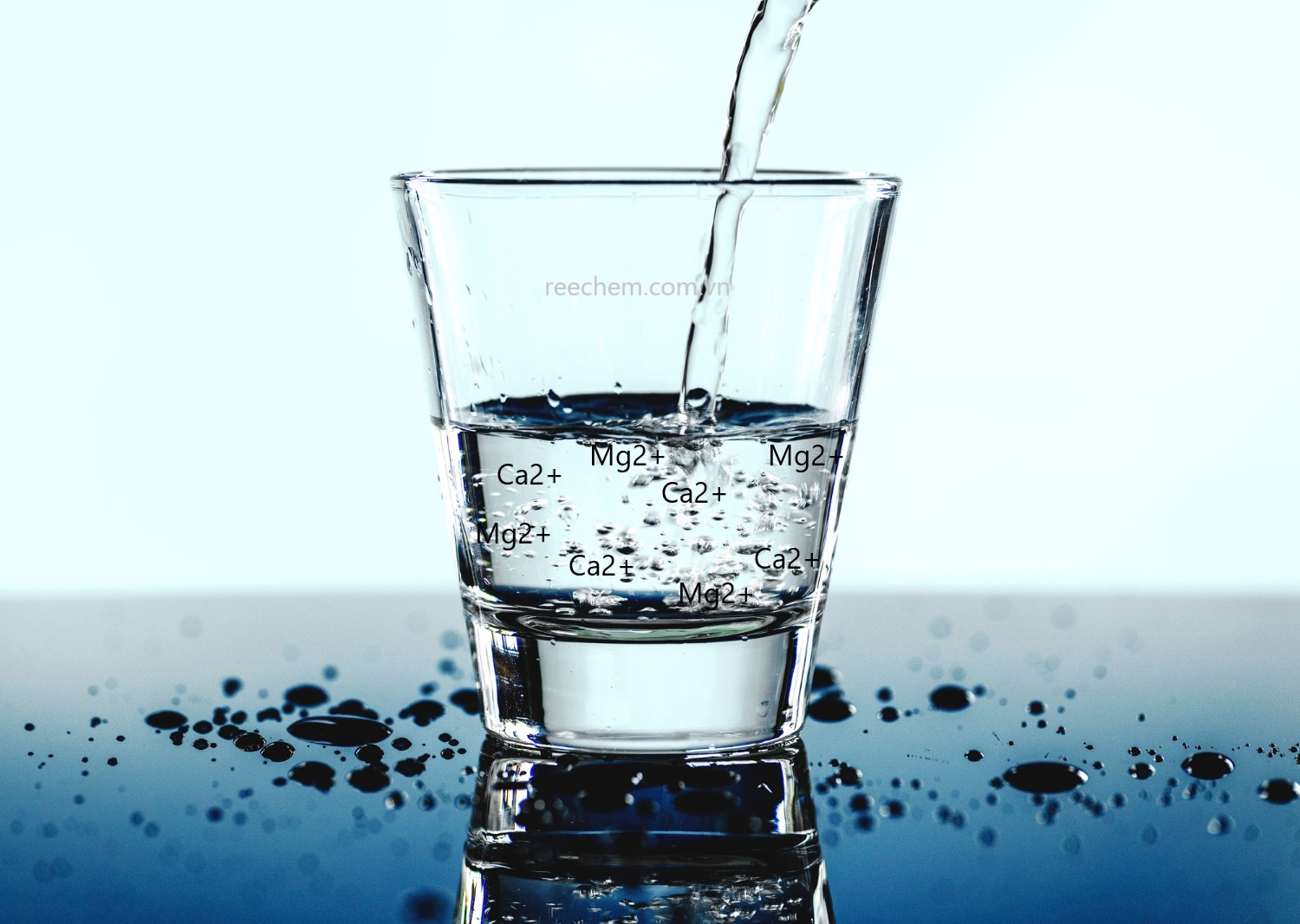

2. Distillation Method
- How it works: Water is boiled, and the steam is condensed back into purified water, free from minerals.
- Advantages: Completely removes hardness and other impurities.
- Disadvantages: High energy costs, not suitable for large-scale treatment.
3. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membrane Filtration Method
- How it works: Uses a reverse osmosis membrane to remove calcium, magnesium, and other contaminants from water.
- Advantages: High efficiency, purified water quality, reduces both hardness and heavy metals.
- Disadvantages: High initial investment costs. Requires regular maintenance and membrane replacement.
4. Chemical Treatment Method
4.1. Using Precipitating Chemicals
- Common chemicals: Soda Ash (Na₂CO₃): Precipitates calcium ions as CaCO₃. Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): Removes temporary hardness.
- Advantages: Effective for high-hardness water and large-scale applications.
- Disadvantages: Requires precise chemical dosage control to prevent excess residues.
4.2. Using Polyphosphates
- How it works: Prevents calcium and magnesium ions from precipitating without removing them.
- Advantages: Easy to use, immediate effectiveness.
5. Electromagnetic Water Softening
- How it works: Uses a magnetic field to alter the structure of calcium and magnesium ions, preventing them from precipitating.
- Advantages: No chemicals required, environmentally friendly. Protects pipes and equipment from scale buildup.
- Disadvantages: Limited effectiveness, depending on water quality.
6. Combined Mechanical Filtration Systems
- How it works: Multi-layer filtration systems using materials like manganese sand, Birm media, and ion exchange resin.
- Advantages: High efficiency, capable of treating multiple water issues.
- Disadvantages: Requires technical expertise for system design and operation.
7. Boiling Method (For Household Use)
- How it works: Temporary hard water is boiled to precipitate calcium and magnesium ions.
- Advantages: Easy to implement at home, no cost.
- Disadvantages: Only effective for temporary hardness, not for permanent hardness.

8. Zeolite Filtration Method
- How it works: Zeolite replaces calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions, similar to ion exchange resins.
- Advantages: Highly effective in softening water.
- Disadvantages: Requires periodic regeneration with NaCl salt.
Conclusion
Each water softening and hardness reduction method has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for different usage needs and treatment scales. For large-scale systems such as boilers, cooling towers, or manufacturing processes, ion exchange and RO membrane filtration are the top choices. Meanwhile, simpler methods like boiling or chemical treatments are more suitable for household use.
If you need expert advice on the best solution for your water source, contact Reechem for support and high-quality products!
📞 Contact Information:
REECHEM COMPANY LIMITED
📍 Address: 5th Floor, Lighthouse Building, 1254 Xô Viết Nghệ Tĩnh, Hòa Cường Nam Ward, Hải Châu District, Da Nang City, Vietnam.
📞 Phone: 0236 391 88 68 / Hotline (Zalo): 0789 086 626
📧 Email: info@reechem.com.vn
🌐 Website: reechem.com.vn















